
trees now planted
BETA CAROTENE
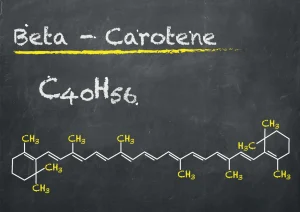 What is beta carotene?
What is beta carotene?
Beta carotene is a natural pigment and provitamin A compound abundant in various fruits and vegetables. It belongs to the carotenoid group, responsible for their vibrant colours. Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, kale, butternut squash, apricots, and mangoes are rich sources of beta carotene.
In the body, beta carotene undergoes enzymatic conversion to vitamin A. Vitamin A is crucial for vision health, immune function, and cellular growth. It supports optimal eyesight, especially in low-light conditions, and helps maintain healthy skin and mucous membranes.
Beta carotene acts as a potent antioxidant, neutralising harmful free radicals. Its ability to combat oxidative stress contributes to overall cellular health and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including certain cancers and heart disease.
Beta carotene, as an antioxidant, has shown benefits for certain ailments. It contributes to reducing the risk of chronic diseases, including certain types of cancer and heart disease, due to its ability to neutralise harmful free radicals. Beta carotene is recognised for its role in supporting vision health and maintaining the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes.
Options that may enhance the body's ability to absorb and utilise beta-carotene for various health benefits:
- Dietary Fat: Beta carotene is a fat-soluble compound, so consuming it with dietary fat can enhance its absorption. Including sources of healthy fats like olive oil, avocados, or nuts in a meal with beta-carotene-rich foods can be beneficial.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C may support the absorption of certain carotenoids, including beta-carotene. Eating foods rich in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, bell peppers, or strawberries, along with beta-carotene-containing vegetables can be a good dietary practice.
DIVE DEEPER
Age |
Male |
Female |
|---|---|---|
|
1 to 3 years: |
1000 IU |
1000 IU |
|
4 to 8 years: |
1335 IU |
1335 IU |
|
9 to 13 years: |
2000 IU |
2000 IU |
|
14 to 18 years: |
3000 IU |
2310 IU |
|
19 to 50 years: |
3000 IU |
2310 IU |
|
51 years and over: |
3000 IU |
2310 IU |
|
During pregnancy: |
|
2,565 IU |
|
Lactation |
|
4,300 IU |




