
trees now planted
GOLD
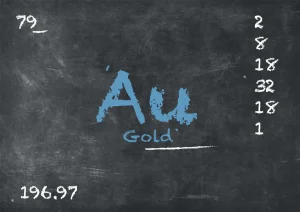
What is gold?
Gold is a precious metal known for its lustrous yellow colour and its high value. It has been treasured and used by humans for thousands of years for various purposes. Gold is highly malleable and ductile, making it easy to shape into different forms, such as jewellery, coins, and decorative items.
It is also an excellent conductor of electricity, which makes it valuable in electronics and telecommunications industries. Gold is relatively ugnisedactive and resistant to corrosion, which contributes to its long-lasting beauty.
Apart from its practical applications, gold has cultural and symbolic significance in many societies and is often associated with wealth, luxury, and prestige.
In 2008, a study was conducted to investigate the effects of gold in the treatment of pathological conditions, particularly rheumatoid arthritis. It has been found that gold can be an effective therapeutic option for this condition. However, the use of injectable gold has been associated with some unfavourable side effects.
Despite this, experts believe that injectable gold holds great potential in the treatment of bone deformities. Further research and development are needed to explore the full therapeutic benefits of gold and to minimise the associated side effects for optimal patient outcomes.
Gold is a pure element and does not naturally combine with other elements to form compounds. Gold is typically found in its native form as nuggets or grains, often embedded in quartz or other minerals. Some of the primary sources and occurrences of naturally occurring gold include:
- Gold Nuggets: Small to large nuggets of pure gold are sometimes found in riverbeds, streams, and alluvial deposits. These nuggets are the result of erosion and weathering of gold-bearing rocks.
- Vein Deposits: Gold can be found in quartz veins and other host rocks. Vein deposits are typically mined underground.
- Placer Deposits: Placer deposits are deposits of gold particles that have been separated from their source rock by natural processes like erosion and carried by water into streams and rivers. Gold panning and sluice mining are common methods of recovering gold from placer deposits.
- Lode Deposits: Lode deposits are gold deposits found in rock formations where gold-bearing minerals are concentrated. These deposits often require underground mining.
- Alluvial Deposits: Gold can be found in sedimentary deposits in riverbeds and floodplains, where it has been transported by water and deposited as alluvium.
- Sedimentary Rocks: In some cases, gold can be found in sedimentary rock layers, especially in areas with ancient riverbeds or sedimentary basins.
- Quartz Veins: Gold is often associated with quartz veins, and miners frequently find gold mixed with quartz or associated with quartz deposits.
- Hydrothermal Deposits: Gold can form in hydrothermal deposits when hot, mineral-rich fluids move through cracks and fissures in the Earth's crust, depositing gold as they cool and react with host rocks.
- Metamorphic Rocks: Gold can be found in certain types of metamorphic rocks, such as schist, gneiss, and slate, where geological processes have concentrated it.
- Secondary Deposits: Some gold deposits are secondary, which means that the gold has been redistributed and concentrated by geological processes, such as weathering and erosion.
Gold, a precious metal known for its beauty and rarity, plays some important roles in the field of medicine and healthcare. Here are some of the medical applications and uses of gold:
- Dental Restorations: Gold has been used in dentistry for many years. It is used to create dental restorations, such as crowns, bridges, and inlays, due to its biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and durability. While other materials like ceramics and composites are more commonly used today for aesthetic reasons, gold remains an option for certain dental applications.
- Intraocular Lenses: Gold is sometimes used in the manufacturing of intraocular lenses (IOLs) implanted during cataract surgery. Gold IOLs are used for their biocompatibility and optical properties.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment: Aurothiomalate and auranofin are gold-containing drugs that have been used in the past for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. These medications are known as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and are used to reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease. However, they are less commonly prescribed today, as newer treatments have become available.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Gold nanoparticles can be used in diagnostic imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT) scans. Gold nanoparticles are introduced into the body and can enhance contrast in CT images, aiding in the detection and diagnosis of certain medical conditions.
- Cancer Treatment (Research): Researchers are exploring the use of gold nanoparticles in cancer treatment. Gold nanoparticles can be targeted to cancer cells and used in photothermal therapy or drug delivery. This area of research is still in the experimental stage and not widely used in clinical practice.
- HIV/AIDS Research: Gold nanoparticles have been studied for their potential use in developing sensitive and rapid diagnostic tests for HIV/AIDS.
- Drug Delivery Systems: Gold nanoparticles can be functionalised to carry drugs or therapeutic agents to specific targets in the body. These nanoparticles can potentially improve the delivery of medications for various medical conditions.


