INFLAMMATION
INFLAMMATION
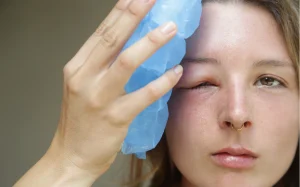
Inflammation is a natural response of the body’s immune system to injury or harmful stimuli. It is a complex process that plays a vital role in protecting and healing tissues. When the immune system detects viruses, bacteria, damaged cells, or toxins, it releases white blood cells and inflammatory cells to the affected area. These cells, along with cytokines, contribute to the inflammatory response.
Inflammation is characterised by redness, pain, temperature changes, and functional limitations. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods and herbs like arnica, clove, fennel, ginger, green tea, lemon, peppermint, and turmeric, as well as essential nutrients such as magnesium, selenium, vitamin D, and zinc, can help support the body’s natural healing process and reduce inflammation.
Description
Inflammation is a natural response of the body to protect itself from harm. It is a complex process involving the immune system and various cells and molecules. Inflammation can occur in response to injury, infection, or chronic conditions.
The signs of inflammation include redness, swelling, heat, pain, and loss of function in the affected area. Acute inflammation is a short-term response that helps in healing and fighting infections. However, chronic inflammation can be harmful and is linked to various diseases such as arthritis, heart disease, and certain cancers.
Lifestyle factors like poor diet, lack of exercise, stress, and smoking can contribute to chronic inflammation. Treatment options include medications to reduce inflammation, lifestyle changes, and natural remedies such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and the use of anti-inflammatory herbs and supplements.
Proper management of inflammation is essential for maintaining overall health and preventing complications.
Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injury or infection, and it typically presents with a combination of the following signs and symptoms:
- Redness (Erythema): Inflammation often causes the affected area to become red or flushed. This is due to increased blood flow to the area as the body's immune cells and chemicals are directed to the site of injury or infection.
- Pain: Inflammation can be accompanied by pain or discomfort in the affected area. Pain is often a result of the release of inflammatory mediators and pressure on nerve endings.
- Heat (Increased Temperature): The inflamed area may feel warm or hot to the touch. This is a result of increased blood flow and metabolic activity as the body works to repair the tissue or combat infection.
- Swelling (Oedema): Swelling or swelling of the affected area is a common sign of inflammation. It occurs as a result of the accumulation of fluid, white blood cells, and proteins at the site of inflammation.
- Loss of Function or Difficulty Using the Affected Area: In some cases, inflammation can lead to decreased or impaired function in the affected body part. For example, joint inflammation (arthritis) can result in stiffness and limited range of motion.
There are two types of inflammation:
- Acute Inflammation: Acute inflammation is a short-term and immediate response that occurs when there is an injury or infection. It is characterised by redness, swelling, heat, pain, and sometimes loss of function in the affected area.
- Chronic Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a long-term inflammatory response that persists for weeks, months, or even years. Unlike acute inflammation, chronic inflammation can be harmful to the body's tissues and organs.
Acute inflammation is a protective and beneficial response, chronic inflammation can be harmful and contribute to the development of various chronic diseases. Inflammation can be triggered by a wide range of factors, and the causes of inflammation can be broadly categorised as follows:
- Injury or Wound: Physical injuries, such as cuts, bruises, burns, and fractures, can lead to inflammation as part of the body's natural healing process. The immune system responds to repair damaged tissue.
- Bacterial or Viral Infection: Infections caused by bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens often trigger inflammation. The immune system's response aims to neutralise and eliminate the invading microbes.
- Autoimmune Disease: Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues and organs. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis are examples of autoimmune diseases characterised by chronic inflammation.
- Autoinflammatory Condition: Autoinflammatory disorders are characterised by recurrent episodes of inflammation without a specific autoimmune cause. Conditions like familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) and periodic fever syndromes fall into this category.
- Food Intolerances or Allergy: Certain individuals may experience inflammation as a result of food intolerances or allergies. When the immune system reacts to specific foods, it can lead to localised or systemic inflammation.
- Obesity: Chronic low-grade inflammation is associated with obesity. Adipose tissue (fat cells) can produce inflammatory molecules, contributing to metabolic and cardiovascular problems.
- Stress: Chronic stress can lead to the release of stress hormones and inflammation in the body. This may contribute to a range of health issues over time.
- Microbiome Imbalance: The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating the immune system and inflammation. An imbalance in the gut microbiota can lead to chronic inflammation and various health problems.
Common medical treatments for inflammation:
- Ibuprofen: Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that helps reduce inflammation, pain, and fever. It works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are chemical messengers that promote inflammation and pain.
- Indomethacin: Indomethacin is another NSAID used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. It's often prescribed for conditions like arthritis, gout, and bursitis.
- Prednisone: Prednisone is a corticosteroid medication that helps reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system's response. It's commonly used to treat a wide range of inflammatory conditions, including autoimmune diseases, allergic reactions, and asthma.
- Immunosuppressants: Immunosuppressant drugs are prescribed to dampen the immune system's activity, which can be overactive in autoimmune diseases and lead to chronic inflammation. Examples include methotrexate, azathioprine, and cyclosporine.
- Topical Creams: Topical anti-inflammatory creams or ointments, such as hydrocortisone creams, are applied directly to the skin to relieve localised inflammation, itching, and redness. They're commonly used for skin conditions like eczema and dermatitis.
Natural treatments for inflammation focus on reducing inflammation through lifestyle and dietary changes. Here's a bit more detail on these natural approaches:
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: An anti-inflammatory diet includes foods that are rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and phytonutrients. Such a diet typically includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like those found in olive oil. It often limits or avoids processed foods, sugary beverages, and foods high in saturated and trans fats.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is important for overall health, including managing inflammation. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps maintain bodily functions and may help reduce inflammation.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health. Aim for a combination of cardiovascular exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises to keep your body active.
- Avoid Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to inflammation in the body. Limiting or avoiding alcohol can be beneficial for managing inflammation.
- No Smoking: Smoking is a major source of inflammation and can exacerbate inflammatory conditions. Quitting smoking can have significant benefits for reducing inflammation and improving overall health.
- Quality Sleep: Adequate, restorative sleep is essential for managing inflammation. Establishing good sleep habits and addressing sleep disorders can help in this regard.
- Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can lead to inflammation. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and relaxation techniques can help reduce stress and its impact on inflammation.
- Identify and Avoid Triggers: If you have specific triggers that worsen inflammation, such as certain foods or environmental factors, identifying and avoiding them can be part of your natural treatment plan.











