ROSACEA
ROSACEA
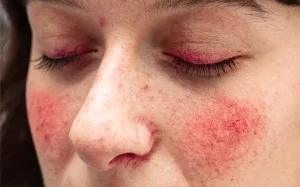
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects fair-skinned women, causing redness, blemishes, and visible blood vessels on the face. It commonly appears on the cheekbones, chin, forehead, and nose.
Flare-ups can be triggered by factors such as sunlight, spicy foods, and emotional stress. While the exact causes are unknown, treatments include topical medications and oral antibiotics to reduce inflammation.
Natural remedies involve practising sun protection, maintaining skin hydration, and avoiding touching the face with dirty hands. Certain foods like chia seeds, green tea, coconut oil, garlic, as well as vitamins and minerals like vitamin A and omega-3, can provide additional support.
Description
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition causing facial redness, inflammation, and visible blood vessels. It commonly affects fair-skinned adults aged 30-50. Triggers like sunlight, weather, spicy foods, and stress can worsen symptoms.
While there is no cure, treatments include topical medications, oral antibiotics, and laser therapy. Skincare practices like gentle cleansing, sunscreen use, and avoiding harsh substances can help manage symptoms.
Lifestyle adjustments and stress management are also important. Rosacea requires personalised care from a dermatologist to develop a suitable treatment plan. With proper management, individuals can control symptoms and improve their skin’s appearance.
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that can manifest with a variety of symptoms, and its presentation can vary from person to person. Here are some common signs and symptoms associated with rosacea:
- Flushing or Persistent Redness: Rosacea often starts with frequent flushing or persistent redness, primarily affecting the central face, including the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead.
- Visible Blood Vessels: Small blood vessels (telangiectasia) may become visible on the skin's surface, appearing as thin red lines or spider-like patterns.
- Acne-Like Bumps: Small, red, and pus-filled bumps (papules and pustules) can develop on the face, giving the appearance of acne. These bumps are a hallmark of rosacea.
- Thicker Skin: Over time, the skin affected by rosacea may thicken and become bumpy, particularly around the nose (rhinophyma). This is more common in severe cases.
- Eye Involvement: Some individuals with rosacea may experience dryness, irritation, and redness in the eyes and eyelids. This condition is known as ocular rosacea and can cause discomfort and vision problems.
- Burning or Stinging Sensation: Many people with rosacea report a burning or stinging sensation in the affected areas of the face.
- Swollen Nose: In some cases, the nose can become swollen and bulbous, a condition known as rhinophyma. This is more common in men.
- Dry, Irritated Skin: Rosacea-prone skin is often sensitive, dry, and prone to irritation. This can make choosing suitable skincare products and routines important.
Rosacea is a complex skin condition with multifactorial causes, and its exact etiology is not fully understood. While the precise cause of rosacea remains elusive, it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some common factors that can trigger or exacerbate rosacea symptoms in susceptible individuals include:
- Genetic Predisposition: There is evidence to suggest that rosacea may have a genetic component, as it often runs in families. People with a family history of rosacea may be more prone to developing the condition.
- Dysregulation of Blood Vessels: Rosacea is associated with the dilation of blood vessels in the skin. Certain triggers, such as hot beverages, spicy foods, or drugs that dilate blood vessels, can lead to flushing and the development of rosacea symptoms.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors like sun exposure, extreme temperatures (both hot and cold), wind, and humidity can trigger or worsen rosacea symptoms. UV radiation from the sun is known to aggravate the condition.
- Emotional Stress: Stress and emotional factors can play a role in rosacea flare-ups. Emotional stress can lead to flushing and increased sensitivity in the skin.
- Microorganisms: Some researchers have explored the role of microorganisms, such as Demodex mites and certain bacteria, in contributing to rosacea. However, the exact relationship is still being studied.
- Cosmetic Products: Some skincare and cosmetic products, particularly those containing harsh or irritating ingredients, can trigger or exacerbate rosacea symptoms in individuals with sensitive skin.
- Dietary Factors: While diet alone is not considered a primary cause of rosacea, certain dietary triggers like hot or spicy foods, alcohol, and hot beverages can lead to flushing and aggravate symptoms in some people.
Medical treatment for rosacea can vary depending on the severity and specific symptoms of the condition. Here are some common medical treatments and medications that may be recommended by healthcare providers:
- Topical Creams or Gels: These medications are applied directly to the skin and can help reduce redness, inflammation, and visible blood vessels associated with rosacea. Brimonidine (Mirvaso) and oxymetazoline (Rhofade) are examples of topical treatments that can temporarily alleviate redness.
- Oral Antibiotics: For more moderate to severe cases of rosacea, oral antibiotics like doxycycline (Oracea) may be prescribed. Antibiotics can help reduce inflammation and control the spread of rosacea symptoms. They are often used in lower doses than when treating infections.
- Oral Isotretinoin (Amnesteem, Claravis): In cases of severe and resistant rosacea, oral isotretinoin may be considered. This medication is a potent retinoid that can help improve skin quality and reduce symptoms, but it may have significant side effects and requires close monitoring by a healthcare provider.
- Other Oral Medications: In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe other oral medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs or medications that target specific aspects of the immune response involved in rosacea.
- Eye Drops: If rosacea affects the eyes and causes dryness, irritation, or inflammation of the eyelids (ocular rosacea), artificial tears or prescription eye drops may be recommended to relieve symptoms.
- Laser or Light Therapy: Certain types of lasers and light-based therapies, such as intense pulsed light (IPL) and pulsed dye lasers, can be effective in reducing visible blood vessels and redness associated with rosacea. These treatments are typically performed by dermatologists or specialists.
- Cleansers and Skincare Products: Healthcare providers may recommend gentle skincare products and cleansers that are specifically formulated for sensitive skin to help manage rosacea symptoms and minimise irritation.
- Sun Protection: Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF is essential for individuals with rosacea to protect their skin from UV radiation, which can exacerbate symptoms.
- Trigger Identification and Management: Identifying and avoiding personal triggers that worsen rosacea symptoms is a crucial aspect of treatment. Patients may be advised to keep a diary of their triggers and modify their lifestyle and diet accordingly.
Natural treatments and lifestyle modifications can complement medical interventions for rosacea and help manage its symptoms. Here are some natural treatment options and practices that may be beneficial for individuals with rosacea:
- Sun Protection: Sunscreen is essential for protecting the skin from UV radiation, which can exacerbate rosacea symptoms. Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, and apply it daily, even on cloudy days.
- Gentle Skincare: Use mild and fragrance-free skincare products suitable for sensitive skin. Avoid harsh or abrasive cleansers and exfoliants that can irritate the skin. Consider using a gentle cleanser and moisturiser formulated for sensitive skin.
- Hand Hygiene: Avoid touching your face with unwashed hands to prevent the transfer of dirt, bacteria, and potential irritants to the skin.
- Hydration: Keep your skin well-hydrated by using a non-irritating moisturiser. Hydrated skin is less likely to become dry, flaky, or prone to irritation.
- Facial Massage: Gentle facial massage can promote blood circulation and relaxation. Be cautious not to apply excessive pressure, as this can aggravate sensitive skin.
- Stress Management: Stress is a known trigger for rosacea flare-ups. Practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels and improve overall well-being.
- Probiotics: Some individuals with rosacea have reported improvements in their skin condition after taking probiotic supplements or consuming probiotic-rich foods. Probiotics may help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, which can influence skin health.
- Trigger Avoidance: Identify and avoid personal triggers that worsen rosacea symptoms. Common triggers include extreme temperatures, wind, hot or spicy foods, alcohol, and certain skincare products. Keeping a diary of triggers can be helpful in pinpointing specific culprits.
- Cool Compresses: Applying a cool, damp cloth or compress to the affected areas can help soothe inflammation and reduce redness temporarily.
- Diet: Some individuals find that dietary modifications, such as reducing spicy foods and alcohol consumption, can help manage their rosacea symptoms. However, the impact of diet can vary from person to person.
- Skin-friendly Makeup: If you use makeup, choose non-comedogenic and hypoallergenic products that are less likely to clog pores or trigger irritation. Mineral-based makeup may be suitable for individuals with rosacea.










