
trees now planted
COPPER
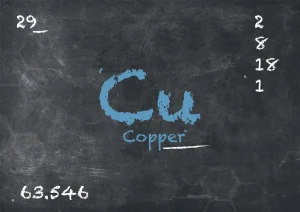
What is copper?
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a reddish-orange metal that has been used by humans for thousands of years due to its desirable properties.
Copper is known for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it widely used in electrical wiring, plumbing systems, and heat exchangers. It is also highly malleable and ductile, allowing it to be easily shaped into various forms.
Copper is found naturally in the Earth’s crust and is commonly extracted from copper ores such as chalcopyrite and bornite. It has numerous applications in industries such as construction, electronics, transportation, and telecommunications.
Furthermore, copper is an essential trace element for living organisms and is involved in various biological processes.
A 2015 study discovered a correlation between low blood copper levels and low bone density in postmenopausal women. As a result, the study recommended the inclusion of copper supplements as part of the treatment regimen to potentially enhance bone density.
In a separate animal study conducted in 2019, copper nanoparticles exhibited promising results in slowing down the growth of pancreatic tumours. Although these findings are encouraging, further research is necessary to validate the effectiveness and safety of copper nanoparticles in treating pancreatic cancer in humans.
These studies highlight the potential therapeutic implications of copper in different health conditions, such as osteoporosis and cancer. However, it is important to note that additional research is needed to fully understand the extent and specific mechanisms of copper's effects in these contexts.
No, however consuming large amounts of zinc (150 mg daily or more ) for several weeks interferes with the bioavailability of copper. Also consuming high amounts of vitamin C (more than 1500 mg per day) interferes with the absorption of copper.
Soluble proteins and carbohydrates enhance the absorption and bioavailability of copper.
Recommended Products
DIVE DEEPER
How much does the body need per day?
Age |
Male |
Female |
|---|---|---|
|
1 to 3 years: |
340 µg |
340 µg |
|
4 to 8 years: |
440 µg |
440 µg |
|
9 to 13 years: |
700 µg |
700 µg |
|
14 to 18 years old: |
890 µg |
890 µg |
|
19 to 50 years: |
900 µg |
900 µg |
|
51 years and over: |
900 µg |
900 µg |
|
During pregnancy: |
|
1000 µg |
|
Lactation |
|
1300 µg |











