LYMPHATIC DISEASE
LYMPHATIC DISEASE
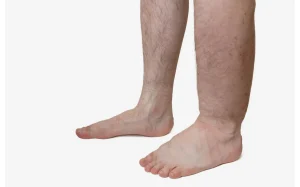
Lymphatic problems encompass conditions like lymphedema and lymphatic obstruction, which involve disruptions in the normal functioning of the lymphatic system. These issues can lead to swelling, particularly in the legs, arms, and skin, and give rise to symptoms such as skin discoloration, limited mobility, and fluid retention.
Lymphedema can be classified into two main types: primary hereditary lymphedema, often caused by genetic mutations, and secondary lymphedema, which can occur after cancer treatment or surgery.
Treatment options for lymphatic problems include surgical interventions, manual lymphatic drainage, and the use of compression garments. Additionally, natural approaches such as exercise, proper hydration, massage, and relaxation techniques can be beneficial.
Incorporating foods that are rich in anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, such as berries, garlic, ginger, and leafy greens, can support lymphatic health. Essential vitamins and minerals like vitamin A, C, D, and omega-3 also play a role in maintaining a healthy lymphatic system.
Description
Lymphatic problems encompass various conditions that impact the lymphatic system, crucial for immune function and fluid balance. These issues, such as lymphedema, lymphadenopathy, and lymphatic obstruction, can result in symptoms and complications.
Lymphedema involves swelling, typically in the limbs, due to fluid build-up. Lymphadenopathy manifests as enlarged lymph nodes from infection or inflammation. Lymphatic obstruction disrupts lymph flow, leading to fluid retention.
Causes include infections, immune disorders, cancer, surgeries, and genetic factors. Symptoms include swelling, pain, recurrent infections, fatigue, and skin changes.
Treatment involves addressing the underlying cause, using compression therapy, exercise, medications, and lifestyle adjustments. Self-care measures like maintaining a healthy weight, proper skin hygiene, physical activity, and stress management support lymphatic health. Early detection, medical care, and a healthy lifestyle enhance well-being in managing lymphatic problems.
Lymphatic diseases can manifest with a variety of symptoms, depending on the specific condition and its severity. Some of the common symptoms associated with lymphatic diseases include:
- Swelling: Swelling, also known as lymphedema, is a hallmark symptom of lymphatic diseases. It often occurs in the legs, arms, fingers, toes, or other parts of the body and is caused by a build-up of lymph fluid.
- Skin Changes: Skin in the affected areas may change in colour, become thickened, or develop a fibrotic texture.
- Limited Mobility: Swelling and fluid accumulation can lead to difficulty moving the affected body parts, which may result in reduced range of motion and discomfort.
- Digestive Problems: In some cases, lymphatic diseases can affect the gastrointestinal system, leading to digestive issues such as diarrhoea, malabsorption, or abdominal pain.
- Skin Lesions: Skin lesions or open sores may develop in areas with chronic lymphedema or lymphatic disorders.
- Persistent Cough: Some lymphatic diseases may involve the respiratory system, leading to a chronic cough or breathing difficulties.
- Recurrent Infections: A compromised lymphatic system can weaken the body's immune response, making individuals more susceptible to recurrent infections, including skin infections.
- Fever: Infections or inflammatory processes associated with lymphatic diseases can cause fever as a symptom.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged and tender lymph nodes may be observed in various parts of the body, such as the neck, armpits, or groin, in response to infections or other lymphatic issues.
- Fatigue: Chronic conditions affecting the lymphatic system may lead to persistent fatigue and a general feeling of tiredness.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss can occur in some cases of lymphatic disease, particularly when there is chronic inflammation or malabsorption.
Common types of lymphatic diseases include:
- Lymphadenopathy: Enlargement or swelling of lymph nodes due to infections, inflammation, or cancer.
- Lymphedema: A condition characterised by swelling, usually in the arms or legs, caused by a blockage or damage to the lymphatic vessels, leading to the accumulation of lymph fluid.
- Lymphangitis: Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels, often caused by bacterial infections, resulting in red streaks on the skin, pain, and fever.
- Castleman Disease: A rare condition that causes enlarged lymph nodes and overgrowth of lymphatic tissue, with two main types: unicentric (affecting a single lymph node) and multicentric (affecting multiple lymph nodes).
- Hodgkin Lymphoma: A type of lymphoma characterised by the presence of specific abnormal cells called Reed-Sternberg cells in the lymph nodes.
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: A group of lymphomas that do not involve Reed-Sternberg cells and can arise in various lymphoid tissues.
- Lymphocytosis: An increase in the number of lymphocytes in the blood, often associated with infections or certain diseases.
- Lymphocytopenia: A decrease in the number of lymphocytes in the blood, which can be caused by various medical conditions, including certain infections, autoimmune diseases, and treatments like chemotherapy.
- Lymphangioma: A benign tumour that forms in the lymphatic vessels or lymph nodes, often present at birth or developing during childhood.
- Lymphoproliferative Disorders: A group of disorders characterised by the excessive growth of lymphocytes, which can include various lymphomas and other related conditions.
- Kikuchi Disease (Histiocytic Necrotizing Lymphadenitis): A rare, self-limiting condition causing swollen and tender lymph nodes, usually accompanied by fever and fatigue.
- Filariasis: A parasitic infection transmitted by mosquitoes, causing lymphatic obstruction and leading to lymphedema and other symptoms.
- Chylous Disorders: Conditions that involve the leakage of chyle, a milky lymphatic fluid, into body cavities or tissues, often caused by trauma, surgery, or certain medical conditions.
Lymphatic diseases can have a variety of causes and contributing factors, depending on the specific condition. Here are some common causes and factors associated with various lymphatic diseases:
- Infections: Infections can affect the lymphatic system, leading to conditions such as lymphangitis or lymphadenitis. Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can invade the lymphatic vessels and nodes.
- Parasitic Infections: Certain parasitic infections, such as filariasis, can directly affect the lymphatic system, causing lymphatic filariasis. These parasites can block lymphatic vessels and lead to lymphedema.
- Radiotherapy: Radiation therapy for the treatment of cancer can damage lymphatic vessels and nodes, leading to lymphedema or other lymphatic complications.
- Metastasis: Cancer cells from primary tumours can spread to the lymph nodes, causing lymph node metastasis. This is a common feature of many types of cancer and can impact lymphatic function.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may have genetic predispositions that make them more susceptible to lymphatic disorders. These genetic factors can influence lymphatic development and function.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical trauma, such as severe injury or surgery, can damage lymphatic vessels or nodes, leading to lymphatic complications.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Autoimmune disorders like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the lymphatic system, leading to inflammation and lymphatic dysfunction.
- Lymphatic Obstruction: Obstruction of lymphatic vessels or nodes can occur due to various reasons, including tumours, scar tissue formation, or inflammation.
- Obesity: Obesity is a risk factor for the development of lymphedema. Excess body weight can put pressure on the lymphatic system and impede lymph flow.
- Complications in Surgery: Surgical procedures that involve the removal of lymph nodes or damage to lymphatic vessels can result in lymphatic complications, including lymphedema.
The medical treatment of lymphatic diseases depends on the specific condition and its underlying cause. Here are some common medical treatments and interventions for lymphatic diseases:
- Conservative Management: In some cases, especially for mild lymphatic disorders, conservative measures may be recommended. This can include lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good skincare, and avoiding tight clothing.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapists can provide manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) therapy, a specialized massage technique that helps stimulate lymphatic flow and reduce swelling.
- Compression Therapy: Compression garments or bandages may be prescribed to help improve lymphatic drainage and reduce edema (swelling).
- Medications: Depending on the underlying condition, medications may be used. For example, antibiotics can be prescribed for lymphangitis (infection of the lymphatic vessels), and diuretics may be used to reduce fluid retention in some cases.
- Surgery: Surgical interventions may be necessary for certain lymphatic diseases. Procedures like lymph node transplantation or lymphovenous anastomosis can help restore lymphatic function.
- Lymphedema Pumps: Devices like pneumatic compression devices or lymphedema pumps can assist in reducing swelling and improving lymphatic flow.
- Radiotherapy: In some cases of lymphatic cancer (lymphoma), radiation therapy may be recommended to target and shrink cancerous lymph nodes.
- Chemotherapy: For aggressive lymphomas and other lymphatic cancers, chemotherapy may be part of the treatment plan.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy drugs can be used to treat certain types of lymphoma by enhancing the body's immune response against cancer cells.
- Lymphatic Drainage Surgery: Complex lymphatic reconstruction surgeries, including lymph node transfers and vascularized lymph node transfers, can be performed for severe cases of lymphedema.
- Treatment of Underlying Causes: Managing the underlying condition that is causing lymphatic disease is often a crucial aspect of treatment. For example, treating infections, managing heart failure, or addressing inflammatory conditions can help alleviate lymphatic symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Patients with lymphatic diseases may need to make lifestyle adjustments to manage their condition effectively. This can include maintaining proper hygiene, avoiding trauma or injury to affected areas, and protecting the skin from infections.
Natural approaches can complement medical treatment for lymphatic diseases and help manage symptoms. Here are some natural strategies that may be beneficial:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can promote lymphatic circulation and reduce swelling.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential for lymphatic function. Drinking an adequate amount of water helps keep lymph fluid flowing efficiently.
- Lymphatic Massage: Lymphatic drainage massage, performed by a trained therapist, can assist in moving lymphatic fluid and reducing swelling. This specialised massage technique is gentle and aims to stimulate lymphatic flow.
- Relaxation and Meditation: Stress management techniques, including relaxation exercises and meditation, may help reduce stress-related symptoms and improve overall well-being. Chronic stress can impact the lymphatic system, so stress reduction is essential.
- Hot and Cold Compresses: Alternating hot and cold compresses on swollen areas can provide relief. Heat can help relax tissues, while cold can reduce inflammation. Always use caution to avoid extreme temperatures.
- Essential Oils: Some essential oils, such as lavender and chamomile, are known for their anti-inflammatory and calming properties. Diluted essential oils can be used for aromatherapy or added to a carrier oil for gentle massage.
- Avoid Tight Clothing: Wearing tight or constrictive clothing can impede lymphatic flow. Opt for loose-fitting garments to allow proper circulation.
- Elevate Affected Limbs: If you have swelling in your arms or legs, elevating them above heart level when resting can help reduce fluid build-up.
- Herbal Supplements: Certain herbal supplements, like horse chestnut and butcher's broom, are believed to support circulation and may be considered as complementary treatments.
- Nutrition: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients to support overall health, including lymphatic function.






