SILVER
SILVER
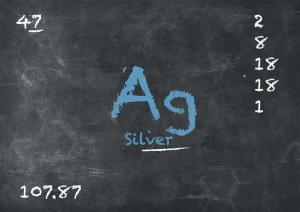
What is silver?
Silver, with its atomic number 47 and atomic symbol Ag, is a lustrous and relatively soft metal that can undergo tarnishing when exposed to air, forming black silver sulphide due to the reaction with sulphur compounds.
Throughout history, silver has been renowned for its antibacterial properties, and in recent times, advancements in biotechnology have further expanded its applications in various medical conditions and treatments.
The antibacterial effect of silver has made it a valuable component in wound dressings, medical devices, and topical preparations, where it helps inhibit the growth of bacteria and promote healing. The unique properties of silver continue to be explored for their potential therapeutic benefits in the field of medicine.
A study conducted in 2018 highlighted the widespread applications of silver in both medicinal and consumer settings, primarily due to its remarkable antimicrobial properties. The research emphasised the growing commercial utilisation of silver in various fields, including medicine, cosmetics, and household products.
The antimicrobial properties of silver make it an effective agent for combating bacteria, viruses, and fungi, thereby contributing to improved hygiene and infection control. The expanding use of silver in these industries reflects the recognition of its potential benefits and the increasing demand for products that prioritise safety and cleanliness.
Silver is a naturally occurring chemical element that is found in various geological and environmental settings. It is typically found in the Earth's crust in association with various minerals and ores. Some common forms and elements in which silver naturally occurs include:
- Silver Minerals: Silver is often present in the form of silver minerals, either in native (pure) form or as compounds.
- Silver-Bearing Ores: Silver can be found in various types of ores, including lead-zinc ores, copper ores, and gold ores. In these ores, silver is often present as a byproduct of mining for other metals.
- Silver-Copper Deposits: Some geological formations are rich in silver-copper deposits, where silver is associated with copper minerals.
- Epithermal Veins: Epithermal veins, which are formed near the Earth's surface, can contain silver along with other minerals like quartz, calcite, and sulfides.
- Base Metal Deposits: Silver is often found in base metal deposits, such as lead and zinc deposits. It can occur as a secondary mineral in these deposits.
- Mining Regions: Historically, silver has been mined from various regions worldwide, including Mexico, Peru, Bolivia, the United States (particularly in states like Nevada and Colorado), and Canada.
- Alluvial Deposits: In some cases, silver particles can be eroded from rocks and deposited in riverbeds and alluvial deposits.
- Sedimentary Rocks: Silver can be present in sedimentary rocks, particularly in areas with hydrothermal activity and mineral deposition.
Silver is used in various medical instruments and devices for its antimicrobial properties and its ability to inhibit the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms. Here are some medical instruments and applications where silver can be found:
- Silver-Coated Catheters: Silver-coated urinary catheters are used to reduce the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in patients. The silver coating helps prevent bacterial colonisation on the catheter's surface.
- Wound Dressings: Silver-containing wound dressings are used to treat chronic wounds, burns, and infections. Silver helps control bacterial growth and promote wound healing.
- Implants and Prostheses: Silver-coated or silver-alloy implants and prosthetic devices are used in orthopaedic and other surgeries to reduce the risk of postoperative infections.
- Silver Nitrate Solution: Silver nitrate solution is used in various medical procedures, including the treatment of warts, removal of granulation tissue, and as an antimicrobial agent in eye care.
- Silver Sulfadiasine Cream: Silver sulfadiasine cream is used in burn care to prevent and treat infections in burn wounds.
- Catheter-Associated Infection Prevention: Some urinary and central venous catheters are impregnated with silver to reduce the risk of catheter-related infections.
- Dental Materials: Silver nanoparticles are used in dental materials, such as fillings and dental composites, to inhibit the growth of bacteria and prevent tooth decay.
- Silver-Coated Endotracheal Tubes: Silver-coated endotracheal tubes are used in critical care settings to reduce the risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia.
- Silver-Based Antimicrobial Dressings: Various silver-based antimicrobial dressings are used for wound care, including silver-impregnated dressings and silver-embedded foam dressings.
- Orthopaedic Implants: Silver-coated orthopaedic implants, such as plates and screws, are used to reduce the risk of post-surgery infections.
- Surgical Instruments: Some surgical instruments may have silver coatings or components to maintain aseptic conditions during procedures.
- Antimicrobial Coatings: Hospital surfaces, medical equipment, and devices may be coated with silver-based antimicrobial coatings to reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections.



