VITAMIN C
VITAMIN C
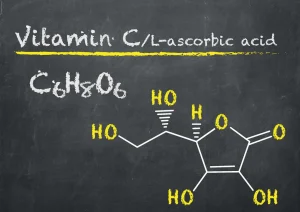
What is vitamin C?
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for various biological processes in the body. It is widely known for its role in supporting immune function and as an antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Vitamin C is involved in collagen synthesis, which is important for the health of connective tissues, skin, and blood vessels. It also aids in the absorption of iron, supports the production of neurotransmitters, and has been linked to potential benefits for cardiovascular health and reducing the duration and severity of the common cold.
Vitamin C is a crucial nutrient that the body requires for proper functioning. Unlike some other animals, humans cannot produce vitamin C on their own and must obtain it from external sources such as food or supplements.
Once consumed, vitamin C is distributed throughout the body, including in the plasma and leukocytes, where it serves as a natural reservoir. It plays a vital role in several metabolic processes, most notably the stimulation of collagen synthesis. Collagen is a protein ot that provides structural support to various tissues, including the skin, blood vessels, bones, and cartilage.
In addition to its role in collagen formation, vitamin C acts as a potent antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by harmful free radicals. It also supports immune function, helps with iron absorption, and participates in numerous other biochemical reactions within the body.
Vitamins or minerals that enhance the absorption of vitamin C include:
- Bioflavonoids: While not minerals, bioflavonoids are compounds found in fruits and vegetables that can enhance the absorption and activity of vitamin C. They work synergistically with vitamin C to improve its antioxidant properties and bioavailability.
- Iron: Vitamin C can enhance the absorption of non-heme iron (the type of iron found in plant-based foods) when consumed together. This is particularly helpful for individuals who follow vegetarian or vegan diets and may have lower iron intake.
- Copper: Copper is involved in various enzymatic reactions in the body, and it may help optimise vitamin C's antioxidant function and collagen formation.
- Zinc: Zinc and vitamin C may work together to support immune function and overall health. Both are essential for proper immune system function, and they can complement each other when taken together.
- Manganese: Manganese is another mineral that can interact with vitamin C, especially in the formation of collagen and bone health.
- Vitamin E: Vitamin E and vitamin C can have a synergistic antioxidant effect in the body, working together to combat oxidative stress.
Recommended Products
DIVE DEEPER
How much does the body need per day?
Age |
Male |
Female |
|---|---|---|
|
0-6 months |
40 mg |
40 mg |
|
7-12 months |
50 mg |
50 mg |
|
1-3 years |
15 mg |
15 mg |
|
4-8 years |
25 mg |
25 mg |
|
9-13 years |
45 mg |
45 mg |
|
14-18 years |
75 mg |
65 mg |
|
19 and above |
90 mg |
75 mg |
|
Pregnant (14-18 years) |
|
80 mg |
|
Pregnant (19 years and above) |
|
85 mg |
|
Lactating (14-18 years) |
|
115 mg |
|
Lactating (19 years and above) |
|
120 mg |













